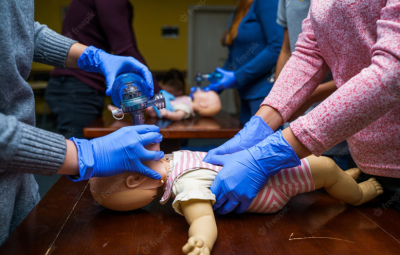
Recognizing when a baby is in danger of dying is not always easy, especially if the symptoms are subtle or masked by other conditions. It’s also difficult to make decisions in an emergency situation, where every second counts and one small mistake can lead to irreparable consequences. This is why standard operating procedures are essential. A neonatal resuscitation program helps healthcare workers perform CPR correctly when assisting infants with respiratory issues, so they have a greater chance of survival even during an emergency. Hospitals that implement this kind of training experience fewer infant deaths and lower mortality rates than those who don’t provide such NRP classes to their staff members. This article outlines why neonatal resuscitation programs are necessary for all well-trained medical professionals, as well as the benefits they bring to hospitals and patients across the country.
Why Neonatal Resuscitation Program Classes are Necessary for Healthcare Workers
If a baby is born prematurely, it’s common for the respiratory system to not be properly developed. This can cause infants to become oxygen-deprived and may even result in a baby dying. Without a resuscitation program, medical professionals may not know how to respond to a baby struggling to breathe. They may panic during an emergency situation, unsure of which steps to take to provide assistance. This can result in a baby not receiving the urgent care they need and dying as a result. A neonatal resuscitation program teaches healthcare workers how to respond when a baby is struggling to breathe, so they know exactly what steps to take to save the infant’s life. Such classes enable healthcare workers to stay calm in an emergency, responding with confidence and the knowledge that they’re doing everything possible to assist the baby. By equipping them with the skills and knowledge necessary to save these infants’ lives, you greatly reduce the risk of death.
The Importance of CPR for Preterm Babies
Preterm babies are at an increased risk of experiencing respiratory issues because their bodies may not be fully developed or able to function properly. This can lead to a serious condition called respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). It’s characterized by fluid building up in a baby’s lungs, making it difficult to breathe. If left untreated, RDS can be fatal. While the exact cause of RDS is unknown, it’s thought to be linked to a lack of surfactant, a substance that keeps the lungs open and functional. Premature babies sometimes don’t produce adequate amounts of surfactant, which is why they’re at higher risk of RDS. A neonatal resuscitation program is essential for healthcare workers treating premature infants, especially those at risk of RDS. It helps them administer CPR correctly by providing specific instructions for each situation and increasing the likelihood of success.
Benefits of Neonatal Resuscitation Program Classes
- Reduces mortality rates: According to research, implementing a neonatal resuscitation program can reduce mortality rates by up to 25%. This equates to a significant reduction in infant deaths, especially those due to respiratory issues.
- Fewer deaths also mean lower medical costs and fewer families experiencing emotional trauma.
- Improves survival rates: Neonatal resuscitation programs also help improve the survival rates of premature infants. They can also reduce the risk of death for full-term infants by as much as 55%.
- Helps staff feel more confident: Along with increasing the likelihood of success, neonatal resuscitation program classes also help staff members feel more confident in their abilities. This can lead to better outcomes for both the parents and the baby by reducing any unnecessary stress.
- Promotes better communication: A neonatal resuscitation program promotes better communication between staff members, which is essential in an emergency situation when every second counts. Communication is especially important when working with premature infants, some of whom are unable-or-unwilling to communicate their feelings or needs.
How to Implement a Successful Resuscitation Program
A neonatal resuscitation program will likely include five key components. These include education and training, simulation, equipment, documentation, and management. - Education and Training: The first step in implementing a neonatal resuscitation program is to educate and train all medical staff members. You should provide information on the most common neonatal conditions, including the appropriate response in each situation. You can also include information on how to handle premature infants. - Simulation: Next, you should simulate neonatal resuscitation situations in a controlled environment to give staff members real-life experience. This will help them better understand what to expect during an emergency. It’ll also allow them to make mistakes without risking the lives of real patients. - Equipment: Neonatal resuscitation programs can also include the use of specialized equipment. This can include things like mannequins, breathing tubes, and suction machines. - Documentation: It’s also important to keep track of all information related to neonatal resuscitation programs, including the number of simulated situations and the results. This data will help you determine if you need to make any changes to your program. - Management: Last but not least, you should manage your neonatal resuscitation program by evaluating how effective it is. You can do this by reviewing the data you collected and determining if changes need to be made. You can also track the number of infant deaths and compare them to the data collected during the neonatal resuscitation program.
Conclusion
Neonatal resuscitation programs are essential for medical staff members treating premature infants. This is because they help healthcare workers respond quickly and correctly when a baby is struggling to breathe. This is critical because babies born prematurely are at an increased risk of developing RDS. Neonatal resuscitation programs can reduce mortality rates and improve survival rates because they equip staff with the knowledge and skills necessary to save an infant’s life. They can also promote better communication between staff members.
 كيفية كتابة رسالة لطلب أو تقديم المشورة: دليل كامل مع أمثلة وعبارات
كيفية كتابة رسالة لطلب أو تقديم المشورة: دليل كامل مع أمثلة وعبارات
 كيفية كتابة رسالة ترشح (للعمل أو التدريب) — نموذج وعبارات مفيدة
كيفية كتابة رسالة ترشح (للعمل أو التدريب) — نموذج وعبارات مفيدة
 كيفية كتابة رسالة اعتذار: دليل شامل مع البنية والتعبيرات الأساسية
كيفية كتابة رسالة اعتذار: دليل شامل مع البنية والتعبيرات الأساسية
 إتقان فن كتابة رسالة شكوى: دليل كامل مع العبارات والأمثلة
إتقان فن كتابة رسالة شكوى: دليل كامل مع العبارات والأمثلة
 كيف تكتب رسالة دعوة
كيف تكتب رسالة دعوة
 For Phd how to write a Letter of appology to a supervisor or an editor
For Phd how to write a Letter of appology to a supervisor or an editor
 شعبية التعليم المنزلي آخذة في الارتفاع في دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة
شعبية التعليم المنزلي آخذة في الارتفاع في دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة
 Free online certification more accessible than ever:
Free online certification more accessible than ever:
 Why Pre school is really important for kids?
Why Pre school is really important for kids?
 كتابة تقارير التدريب مع مثال: تنسيق وخطة ومثال لتقرير التدريب
كتابة تقارير التدريب مع مثال: تنسيق وخطة ومثال لتقرير التدريب
 الوثائق ومتطلبات الحصول على تأشيرة الدراسة في فرنسا
الوثائق ومتطلبات الحصول على تأشيرة الدراسة في فرنسا
 تعرف كيف تجد مشرف رسالة في فرنسا.
تعرف كيف تجد مشرف رسالة في فرنسا.
 منح دراسية في فرنسا ممولة بالكامل باكلوريوس ، ماجستير ، دكتوراه: دعوة سنوية للتقديم
منح دراسية في فرنسا ممولة بالكامل باكلوريوس ، ماجستير ، دكتوراه: دعوة سنوية للتقديم
 رابط إلى 10 + منح دراسية في كندا للطلاب الدوليين
رابط إلى 10 + منح دراسية في كندا للطلاب الدوليين